
In today’s world, safety is paramount, especially when it comes to our vehicles. With advancements in technology, modern cars offer a plethora of safety features that go beyond the traditional airbags and seatbelts. From active systems that help prevent accidents to passive features that mitigate the impact if an accident does occur, understanding these safety technologies is crucial when making a car purchase.
This guide explores the top safety features to look for when buying a new car, providing you with the knowledge to make an informed decision.
We’ll delve into the world of active and passive safety features, examining their functionalities, benefits, and limitations. We’ll also discuss the importance of independent safety ratings and testing, ensuring you understand the safety standards of different car models. By the end of this guide, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge to prioritize safety and make a confident car buying decision.
Safety Features in Modern Vehicles
In today’s world, safety is paramount, and this extends to our vehicles. As technology advances, cars are becoming increasingly sophisticated, incorporating a wide range of safety features designed to protect drivers, passengers, and other road users. Understanding these features and their importance is crucial when purchasing a new car. This guide will highlight some of the most important safety features to consider, helping you make an informed decision.
Active Safety Systems
Active safety systems are designed to prevent accidents from happening in the first place. These systems use sensors, cameras, and other technologies to monitor the surrounding environment and intervene when necessary.
- Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB): AEB systems use sensors to detect potential collisions and automatically apply the brakes if the driver fails to react in time. This feature has been proven to significantly reduce rear-end collisions, a leading cause of accidents.
- Lane Departure Warning (LDW): LDW systems use cameras or sensors to monitor lane markings and alert the driver if the vehicle drifts out of its lane unintentionally. This feature is particularly useful for long drives or in situations where driver fatigue may be a factor.
- Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC): ACC systems allow the driver to set a desired speed and distance from the vehicle ahead. The system automatically adjusts the vehicle’s speed to maintain a safe distance, even in stop-and-go traffic. This feature can reduce driver fatigue and stress, especially during long commutes.
- Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM): BSM systems use sensors to detect vehicles in the driver’s blind spots. The system alerts the driver with visual or auditory warnings when another vehicle is detected. This feature can help prevent accidents when changing lanes or merging into traffic.
- Rear Cross-Traffic Alert (RCTA): RCTA systems use sensors to detect vehicles approaching from the sides when reversing. The system alerts the driver with visual or auditory warnings, helping to prevent collisions when backing out of driveways or parking spaces.
Passive Safety Features
Passive safety features are designed to protect occupants in the event of a crash. These features are often incorporated into the vehicle’s structure and design.
- Airbags: Airbags are inflatable safety devices designed to cushion occupants during a crash. Modern vehicles typically have multiple airbags, including frontal, side, and curtain airbags.
- Seatbelts: Seatbelts are essential safety devices that restrain occupants during a crash. Modern vehicles often include features like pretensioners and load limiters, which further enhance seatbelt effectiveness.
- Stronger Vehicle Structure: Modern vehicles are designed with a stronger, more rigid structure to better absorb impact forces during a crash. This helps to protect occupants from injury by spreading the force of the impact over a wider area.
- Anti-Whiplash Headrests: These headrests are designed to reduce the severity of whiplash injuries in rear-end collisions. They are typically adjustable and can be moved closer to the occupant’s head for optimal protection.
Other Important Safety Features
In addition to active and passive safety systems, there are other features that contribute to overall vehicle safety.
- Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS): TPMS systems monitor tire pressure and alert the driver if any tires are underinflated. Underinflated tires can affect vehicle handling and increase the risk of accidents.
- Backup Camera: Backup cameras provide a rearward view, helping the driver see objects behind the vehicle. This feature can significantly reduce the risk of backing accidents, especially when parking or maneuvering in tight spaces.
- Daytime Running Lights (DRLs): DRLs increase the visibility of the vehicle during daylight hours, making it easier for other drivers to see the vehicle. This feature can help prevent accidents, especially in situations with reduced visibility.
Active Safety Features
Active safety features go beyond passive safety systems, which are designed to protect occupants in the event of a crash. Instead, active safety features are designed to prevent accidents in the first place. These features use sensors, cameras, and other technologies to monitor the vehicle’s surroundings and intervene to avoid collisions.
Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS)
Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) are a collection of technologies that assist drivers with various tasks, enhancing safety and comfort. ADAS features use sensors, cameras, and software to monitor the vehicle’s surroundings, detect potential hazards, and provide warnings or take corrective actions to avoid accidents.
“ADAS is a broad term that encompasses a wide range of features, from basic driver alerts to more advanced systems that can control the vehicle’s steering, braking, and acceleration.”
National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA)
Examples of ADAS Features
ADAS features are becoming increasingly common in modern vehicles, and their use is expected to expand further in the coming years. Some of the most common ADAS features include:
- Lane Departure Warning (LDW): LDW systems use cameras or sensors to monitor the vehicle’s position within its lane. If the vehicle begins to drift out of its lane without the driver’s input, the system will issue a visual or audible warning. Some systems may also provide steering assistance to gently guide the vehicle back into its lane.
- Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC): ACC systems use radar or lasers to maintain a safe distance from the vehicle ahead. They can automatically adjust the vehicle’s speed to maintain a pre-set distance from the vehicle in front, even in stop-and-go traffic. ACC can help reduce driver fatigue and improve fuel efficiency.
- Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB): AEB systems use sensors to detect potential collisions. If the system determines that a collision is imminent, it will automatically apply the brakes to avoid or mitigate the impact. AEB systems can be particularly helpful in situations where drivers may not have time to react, such as when approaching a stopped vehicle or a pedestrian crossing the road.
Passive Safety Features
Passive safety features are designed to protect occupants in the event of a crash. They work by absorbing energy and reducing the forces that act on the driver and passengers.
Types of Passive Safety Features
- Airbags are designed to inflate rapidly during a collision, creating a cushion between the occupants and the steering wheel, dashboard, or other hard surfaces in the vehicle. Airbags are typically deployed in frontal, side, and curtain configurations.
- Seatbelts are designed to restrain occupants during a crash, preventing them from being thrown around the vehicle. Seatbelts are typically equipped with pretensioners and load limiters, which help to reduce the forces on the occupants during a collision.
- Crumple Zones are designed to absorb energy during a crash by collapsing in a controlled manner. This helps to reduce the forces that are transmitted to the occupants.
Airbag Types
- Frontal Airbags are the most common type of airbag. They are located in the steering wheel and dashboard, and they deploy to protect the driver and front passenger from head and chest injuries in a frontal collision.
- Side Airbags are designed to protect occupants from side impacts. They are typically located in the doors and seats, and they deploy to protect the head, chest, and hips from injuries.
- Curtain Airbags are designed to protect occupants from head injuries in a rollover crash. They are typically located in the roofline of the vehicle, and they deploy to create an inflatable curtain that protects the head and neck of the occupants.
Comparison of Airbag Types
| Airbag Type | Deployment Location | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Frontal Airbags | Steering wheel, dashboard | Protect driver and front passenger from head and chest injuries in a frontal collision. |
| Side Airbags | Doors, seats | Protect occupants from side impacts. |
| Curtain Airbags | Roofline | Protect occupants from head injuries in a rollover crash. |
Key Safety Features of Various Car Models
The following table summarizes the key safety features of various car models. Please note that this is not an exhaustive list, and the specific safety features available on a particular model may vary depending on the trim level and year of manufacture.
| Car Model | Frontal Airbags | Side Airbags | Curtain Airbags | Seatbelt Pretensioners | Crumple Zones | Other Safety Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toyota Camry | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Lane Departure Warning, Automatic Emergency Braking |
| Honda Accord | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Adaptive Cruise Control, Blind Spot Monitoring |
| Ford Fusion | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Lane Keeping Assist, Rear Cross Traffic Alert |
| Chevrolet Malibu | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Teen Driver Technology, Automatic Parking Assist |
Safety Ratings and Testing
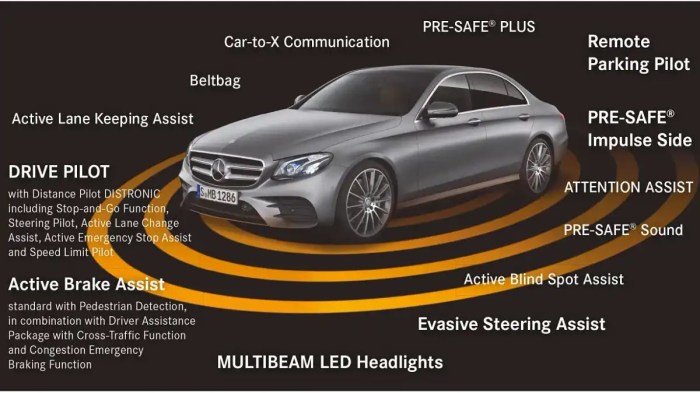
Understanding the safety ratings and testing procedures of independent organizations is crucial when choosing a new car. These organizations provide objective assessments of vehicle safety, helping consumers make informed decisions.
Independent Safety Organizations
Independent safety organizations play a vital role in evaluating the safety of vehicles. These organizations conduct rigorous testing and assign ratings based on their findings. This information helps consumers make informed decisions about vehicle safety.
- IIHS (Insurance Institute for Highway Safety): The IIHS is a non-profit organization that focuses on vehicle safety research and testing. They conduct a wide range of crash tests, including frontal offset, side impact, roof strength, and head restraints.
- NHTSA (National Highway Traffic Safety Administration): The NHTSA is a government agency responsible for vehicle safety regulations and standards. They conduct crash tests and assign safety ratings based on vehicle performance in various crash scenarios.
Safety Tests
Both the IIHS and NHTSA conduct a variety of crash tests to assess a vehicle’s safety performance. These tests simulate real-world crash scenarios and evaluate the vehicle’s ability to protect occupants.
- Frontal Offset Crash Test: This test simulates a head-on collision with another vehicle, with a 40% overlap on the driver’s side. The test measures the vehicle’s ability to protect the driver and front passenger.
- Side Impact Crash Test: This test simulates a collision with another vehicle striking the driver’s side of the vehicle. The test measures the vehicle’s ability to protect the driver and passengers from side impacts.
- Roof Strength Test: This test measures the roof’s ability to withstand a rollover. The test evaluates the roof’s strength and its ability to protect occupants in a rollover crash.
- Head Restraint Test: This test evaluates the effectiveness of head restraints in preventing whiplash injuries in rear-end collisions.
Safety Ratings
Based on the results of their crash tests, both the IIHS and NHTSA assign safety ratings to vehicles. These ratings provide a concise overview of a vehicle’s safety performance.
- IIHS Top Safety Pick+: This rating is awarded to vehicles that achieve the highest ratings in all IIHS crash tests, including the front crash prevention test.
- IIHS Top Safety Pick: This rating is awarded to vehicles that achieve the highest ratings in all IIHS crash tests, except for the front crash prevention test.
- NHTSA 5-Star Safety Rating: This rating is awarded to vehicles that achieve the highest scores in all NHTSA crash tests.
“Safety ratings are based on the performance of a vehicle in controlled crash tests, which may not accurately reflect real-world crashes.”
Additional Safety Considerations

Beyond the core active and passive safety features, several other factors contribute significantly to overall vehicle safety. These aspects often receive less attention but are crucial for ensuring a secure driving experience.
Child Safety
Child safety is paramount, and vehicles offer various features to protect young passengers.
- Child Safety Locks: These locks prevent children from opening doors from the inside, ensuring they remain secure during travel. They are typically located on the rear doors and can be activated with a button or switch.
- LATCH (Lower Anchors and Tethers for Children) System: This system provides standardized anchor points for car seats, ensuring proper installation and secure attachment. The LATCH system is usually found on the rear seats and includes lower anchors and tether straps.
- Rear-Facing Car Seats: Keeping infants and toddlers rear-facing for as long as possible is recommended, as it provides superior head and neck protection in a crash. Many vehicles offer rear-facing car seat compatibility, and some even feature rear-facing seats that can be installed in the front passenger seat.
Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS)
Tire pressure plays a crucial role in vehicle handling, braking, and fuel efficiency.
- Direct TPMS: This system uses sensors embedded in each tire to monitor pressure directly and transmit the data to the vehicle’s computer. It provides real-time readings on the dashboard, alerting the driver to any pressure discrepancies.
- Indirect TPMS: This system relies on the vehicle’s anti-lock braking system (ABS) sensors to infer tire pressure based on wheel speed variations. While less accurate than direct TPMS, it still provides a warning if pressure drops significantly.
Headlights
Effective headlights are essential for safe driving, especially during nighttime or low-visibility conditions.
- High-Intensity Discharge (HID) Headlights: These headlights produce a brighter and whiter light than traditional halogen bulbs, enhancing visibility and reducing eye strain. HID headlights are often associated with higher fuel efficiency and a longer lifespan.
- Light-Emitting Diode (LED) Headlights: LED headlights offer even brighter illumination than HID, consume less energy, and last longer. They also provide faster response times and sharper light patterns, improving visibility and reducing glare.
- Adaptive Headlights: This technology automatically adjusts the headlight beam pattern based on steering angle and speed, illuminating the road more effectively in curves and turns. It helps prevent glare for oncoming traffic and enhances visibility in challenging conditions.
Vehicle Size and Weight
The size and weight of a vehicle can significantly impact its safety performance.
- Larger Vehicles: Larger vehicles generally offer more protection for occupants in a crash, due to their increased mass and crumple zones. They can also provide a better view of the road and other vehicles.
- Smaller Vehicles: Smaller vehicles tend to be more fuel-efficient and maneuverable but may offer less protection in a crash. Their lighter weight can make them more susceptible to rollovers and impact forces.
- Weight Distribution: The distribution of weight within a vehicle also influences safety. Vehicles with a low center of gravity are less likely to roll over, while those with a higher center of gravity may be more prone to rollovers.
Vehicle Maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential for maintaining a vehicle’s safety throughout its lifespan.
- Regular Inspections: Schedule regular inspections to ensure all safety features are functioning properly. This includes checking brakes, tires, lights, steering, and suspension.
- Tire Maintenance: Maintain proper tire pressure and tread depth to ensure optimal handling and braking performance. Rotate tires regularly to promote even wear.
- Fluid Checks: Regularly check engine oil, brake fluid, coolant, and power steering fluid levels. Ensure all fluids are at the correct levels and in good condition.
- Brakes: Inspect brake pads and rotors for wear and tear. Replace them as needed to maintain effective braking performance.
Business Services
Safety features are not only crucial for individual consumers but also play a vital role in various industries, contributing to the safety of workers, equipment, and the environment. These features help businesses mitigate risks, improve productivity, and enhance their overall reputation.
Safety Features in Different Industries
Safety features are essential for industries like automotive, aerospace, and agriculture, where potential hazards are inherent in their operations. Here’s a breakdown of how safety features are implemented across these sectors:
| Industry | Safety Features |
|---|---|
| Automotive |
|
| Aerospace |
|
| Agriculture |
|
Examples of Business Success through Safety Features
Safety features contribute to business success by:
- Reducing Accidents and Injuries: Implementing safety features like airbags, anti-lock brakes, and stability control in vehicles significantly reduces the likelihood of accidents and injuries, minimizing costs associated with medical expenses, insurance claims, and legal liabilities. This is especially important for companies operating in industries like transportation and logistics, where safety is paramount.
- Improving Productivity: In the construction and manufacturing industries, safety features such as machine guarding, safety interlocks, and personal protective equipment (PPE) help prevent accidents and injuries, allowing workers to operate efficiently without fear of harm. This leads to increased productivity and reduced downtime.
- Enhancing Reputation: Companies that prioritize safety and invest in safety features often enjoy a positive public image, as customers and stakeholders value businesses that demonstrate a commitment to safety. This can lead to increased brand loyalty, customer trust, and overall business success.
- Meeting Regulatory Requirements: Many industries are subject to strict safety regulations, and businesses must comply with these regulations to operate legally. Implementing safety features helps companies meet these requirements, avoiding potential fines and penalties.
Investing in a car with comprehensive safety features is an investment in your well-being and peace of mind. By understanding the various safety technologies available, you can make an informed decision that prioritizes safety without compromising on the features and style you desire. Remember, a safe car is not just a luxury, it’s a necessity in today’s world.
So, before you head to the dealership, take the time to research and learn about the safety features that will keep you and your loved ones protected on the road.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between active and passive safety features?
Active safety features aim to prevent accidents by assisting the driver, while passive safety features focus on mitigating the impact of an accident.
Are all safety features standard in every car?
No, safety features can vary significantly between car models and trim levels. It’s important to check the specific features included in the car you’re considering.
How can I learn more about the safety ratings of a specific car?
You can find safety ratings from independent organizations like the IIHS (Insurance Institute for Highway Safety) and the NHTSA (National Highway Traffic Safety Administration) on their respective websites.
What is the importance of a car’s crumple zones?
Crumple zones are designed to absorb impact energy in a collision, protecting the occupants by preventing the passenger cabin from being crushed.





