
Navigating the world of chemicals can be daunting, but understanding Safety Data Sheets (SDS) is essential for ensuring a safe and healthy workplace. These comprehensive documents provide vital information about the hazards associated with specific chemicals, offering guidance on safe handling, storage, and emergency procedures. From manufacturing plants to research labs, SDS play a critical role in protecting employees from potential risks.
This guide aims to demystify SDS, providing a clear understanding of their components, how to interpret hazard information, and how to utilize them effectively in the workplace. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or just starting your career, understanding SDS is crucial for promoting a safe and compliant work environment.
Introduction to SDS
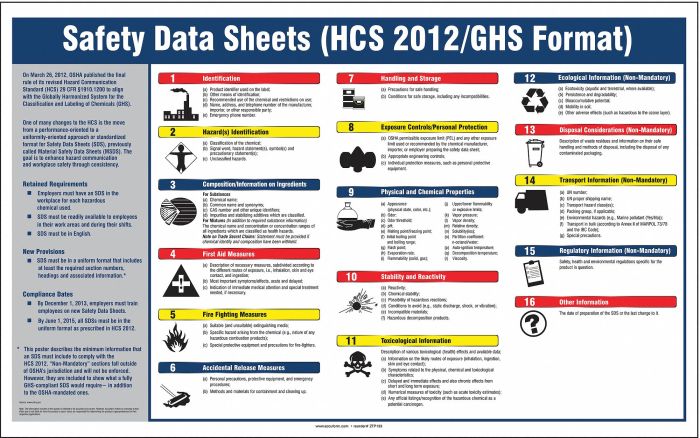
Safety Data Sheets (SDS) are comprehensive documents that provide detailed information about the hazards associated with a chemical product. They are designed to communicate the potential risks of handling, storing, transporting, and using a chemical. SDS are crucial for workplace safety because they provide the necessary information to ensure the safe handling and use of chemicals. They serve as a vital resource for workers, employers, emergency responders, and other stakeholders involved in chemical management.
Industries Where SDS are Critical
SDS are essential in a wide range of industries where chemicals are used, including:
- Manufacturing
- Construction
- Healthcare
- Agriculture
- Transportation
- Research and development
- Education
In these industries, SDS play a vital role in protecting workers, the environment, and the public from the potential hazards of chemicals. They provide essential information about the risks associated with specific chemicals and guide appropriate safety measures.
Safe Handling and Storage
The information on the SDS provides critical guidance on how to safely handle and store chemicals to prevent accidents, injuries, and environmental contamination. Proper handling and storage practices are essential for minimizing the risk of exposure to hazardous substances and ensuring the safety of yourself and others.
Safe Handling Practices
Safe handling practices vary depending on the specific chemical and its hazards. Here are some general guidelines to follow:
- Read the SDS thoroughly before handling any chemical. The SDS will Artikel the specific hazards associated with the chemical, including its flammability, corrosiveness, toxicity, and reactivity.
- Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves, goggles, respirators, and lab coats, as recommended by the SDS. This will help protect you from skin, eye, and respiratory exposure.
- Work in a well-ventilated area, especially when handling volatile chemicals. Adequate ventilation helps to minimize the concentration of harmful vapors in the air.
- Avoid contact with skin, eyes, and clothing. If contact occurs, immediately wash the affected area with plenty of water and seek medical attention if necessary.
- Store chemicals in their original containers, properly labeled with the chemical name, hazard warnings, and any other relevant information.
- Do not mix chemicals unless specifically instructed to do so. Mixing chemicals can create unexpected and dangerous reactions.
- Handle chemicals carefully and avoid spills. If a spill occurs, follow the cleanup procedures Artikeld in the SDS.
Examples of Safe Handling Practices for Different Types of Chemicals
- Flammable liquids: Store flammable liquids in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from heat and ignition sources. Use explosion-proof electrical equipment and avoid static electricity buildup.
- Corrosive chemicals: Handle corrosive chemicals with caution, wearing appropriate PPE, such as gloves and eye protection. Store corrosive chemicals in a separate area, away from other chemicals, and ensure proper ventilation.
- Toxic chemicals: Work with toxic chemicals in a fume hood or other well-ventilated area. Use appropriate PPE, including respirators, to minimize inhalation exposure. Dispose of toxic chemicals according to the SDS and local regulations.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
The SDS provides specific recommendations for PPE based on the chemical’s hazards. It’s crucial to select and use the appropriate PPE to protect yourself from exposure. Here are some examples:
- Gloves: Choose gloves made of a material that is resistant to the specific chemical being handled. Different materials offer varying levels of protection against different chemicals.
- Goggles: Use goggles that provide adequate protection from splashes or fumes. Choose goggles with chemical-resistant lenses and side shields.
- Respirators: Respirators are used to protect against inhalation of hazardous substances. The type of respirator needed depends on the specific hazards of the chemical. Ensure that the respirator is properly fitted and maintained.
- Lab coats: Lab coats provide a barrier between your clothing and the chemicals you are working with. Choose lab coats made of a material that is resistant to the chemicals you will be handling.
Emergency Procedures

Knowing how to respond in an emergency situation is crucial for the safety of everyone involved. The SDS provides detailed instructions for handling spills, leaks, and accidental exposures, ensuring that appropriate actions are taken to minimize risks and protect individuals.
First Aid Measures
First aid measures are essential for addressing immediate health concerns following an accidental exposure to a chemical. The SDS details the specific first aid procedures to be followed, which may include:
- Removing contaminated clothing and washing the affected area with soap and water.
- Administering artificial respiration if breathing has stopped.
- Providing oxygen if needed.
- Seeking immediate medical attention.
It’s important to note that the specific first aid measures will vary depending on the chemical involved. Therefore, it’s crucial to consult the SDS for the specific chemical being handled to ensure appropriate actions are taken.
Emergency Contact Information
The SDS provides emergency contact information for reporting incidents and seeking immediate assistance. This information is crucial for ensuring prompt and effective response in emergency situations.
- Emergency Phone Numbers: The SDS includes emergency phone numbers for contacting relevant authorities, such as poison control centers, fire departments, or medical professionals. These numbers should be readily accessible and prominently displayed in the workplace.
- Emergency Contact Persons: The SDS may also include contact information for designated emergency response personnel within the organization. These individuals are trained and equipped to handle emergency situations and can provide guidance and support during an incident.
In case of an emergency, it’s essential to contact the appropriate emergency response personnel immediately. Providing them with accurate information about the chemical involved, the nature of the incident, and the location of the incident will enable them to provide the most effective assistance.
SDS Access and Management
Making sure that Safety Data Sheets (SDS) are easily accessible and kept up-to-date is crucial for worker safety. This section will explore different methods for managing SDS in the workplace, emphasizing the importance of readily available and current information.
Methods for Accessing and Managing SDS
There are several ways to access and manage SDS in the workplace, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
- Online Databases: Many companies use online databases to store and manage SDS. These databases offer centralized access, allowing employees to easily search for specific SDS using s or chemical names. They also make it easier to update SDS as new information becomes available.
- Physical Files: Traditionally, SDS were stored in physical binders or files. While this method is still used by some companies, it can be challenging to keep track of updates and ensure that the most recent version is readily available. It also requires dedicated space for storage.
- Software Applications: Specialized software applications designed for SDS management can help streamline the process. These applications can automate tasks like updating SDS, generating reports, and providing alerts when SDS need to be reviewed. They also often offer features like mobile access, allowing employees to view SDS from their smartphones or tablets.
Importance of Keeping SDS Up-to-Date
It is essential to keep SDS up-to-date to ensure that employees have access to the most accurate and current information about the hazards associated with the chemicals they work with. Changes in regulations, new scientific findings, or modifications to a chemical’s formulation can all necessitate updates to the SDS.
- Changes in Regulations: Regulatory bodies like OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) regularly update regulations and standards for chemical safety. These changes may affect the information included in SDS, such as the classification of hazards or the required personal protective equipment.
- New Scientific Findings: Research into the health effects of chemicals is constantly evolving. New scientific findings may reveal previously unknown hazards or alter the understanding of existing hazards. These findings can necessitate revisions to SDS to reflect the latest scientific knowledge.
- Modifications to Chemical Formulations: Chemical manufacturers may modify the formulation of a chemical to improve its performance or address environmental concerns. These modifications can affect the hazards associated with the chemical and require updates to the SDS.
Role of Training and Communication
Effective training and communication are crucial for ensuring employees understand how to access, interpret, and utilize SDS information. Employees should be trained on the following:
- Location of SDS: Employees should know where to find SDS, whether it’s in a physical file, an online database, or a software application.
- SDS Format and Structure: Employees should understand the format and structure of SDS, including the different sections and the information they contain.
- Interpreting SDS Information: Employees should be trained on how to interpret the information in SDS, including identifying hazards, understanding safety precautions, and recognizing emergency procedures.
- Using SDS for Workplace Safety: Employees should understand how to use SDS to make informed decisions about safe handling, storage, and disposal of chemicals.
SDS and Business Services
Safety Data Sheets (SDS) play a crucial role in various business sectors, ensuring the safe handling and use of hazardous materials. They provide essential information about chemical hazards, safety precautions, and emergency procedures, contributing to a safer workplace environment.
SDS in Business Services
The importance of SDS in business services is evident in sectors like cleaning, maintenance, and property management, where employees often handle chemicals for cleaning, disinfecting, and pest control. SDS help these businesses comply with relevant regulations, ensuring the safety of employees and the public. For instance, a cleaning company would use SDS to understand the hazards associated with cleaning products, proper storage procedures, and emergency response protocols in case of spills or accidents.
This information enables them to implement appropriate safety measures, train employees, and manage potential risks effectively.
SDS in Aerospace and Defense
The aerospace and defense industry relies heavily on specialized materials and chemicals, making SDS crucial for maintaining workplace safety. These industries often deal with hazardous materials like solvents, adhesives, and paints, requiring detailed information about their properties and handling procedures. SDS help manufacturers and contractors identify potential risks, implement appropriate safety protocols, and train personnel to handle these materials safely.
For example, an aerospace company might use SDS to understand the hazards associated with using specific types of paints or adhesives, including potential health risks, flammability, and proper ventilation requirements.
SDS in Agriculture and Forestry
The agriculture and forestry sectors use a wide range of chemicals, including pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers. SDS provide essential information about the hazards associated with these chemicals, helping to ensure the safety of workers and the environment. This information helps farmers and forestry workers understand the potential risks of using these chemicals, implement appropriate safety measures, and minimize environmental impacts.
For example, a farmer might use SDS to understand the hazards associated with using a specific herbicide, including potential health risks, proper application techniques, and environmental precautions.
SDS in Automobiles and Motorcycles
The automotive industry uses various chemicals in manufacturing, repair, and maintenance, including paints, solvents, and lubricants. SDS help manufacturers, repair shops, and dealerships ensure the safe handling and use of these chemicals, protecting employees and customers. For example, a car dealership might use SDS to understand the hazards associated with using specific types of paints or solvents, including potential health risks, flammability, and proper ventilation requirements.
SDS in Chemicals and Allied Products
The chemical industry, being the primary producer of hazardous materials, heavily relies on SDS to ensure the safe handling and use of its products throughout the supply chain. These industries use SDS to communicate information about chemical hazards, safety precautions, and emergency procedures to customers, distributors, and other stakeholders. This information helps ensure the safe handling and transportation of chemicals, minimizing risks to workers, consumers, and the environment.
For example, a chemical manufacturer might use SDS to provide detailed information about the hazards associated with a specific chemical, including potential health risks, flammability, and proper storage procedures.
By understanding the information contained within SDS and implementing the recommended safety procedures, employees can significantly reduce the risk of chemical hazards in the workplace. The knowledge gained from this guide empowers individuals to make informed decisions regarding their safety, contributing to a culture of workplace safety and compliance.
FAQ Guide
What are the penalties for not following SDS guidelines?
Penalties can vary depending on the jurisdiction and severity of the violation. They may include fines, legal action, and even imprisonment in some cases. It’s essential to consult local regulations and industry standards for specific details.
Where can I find more information about SDS?
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) are excellent resources for comprehensive information about SDS and workplace safety.
How often should SDS be reviewed and updated?
SDS should be reviewed and updated regularly, especially when new information becomes available about the chemical or its hazards. It’s also crucial to update SDS when there are changes in the workplace, such as new procedures or equipment.





